About Scarboroughs Rope
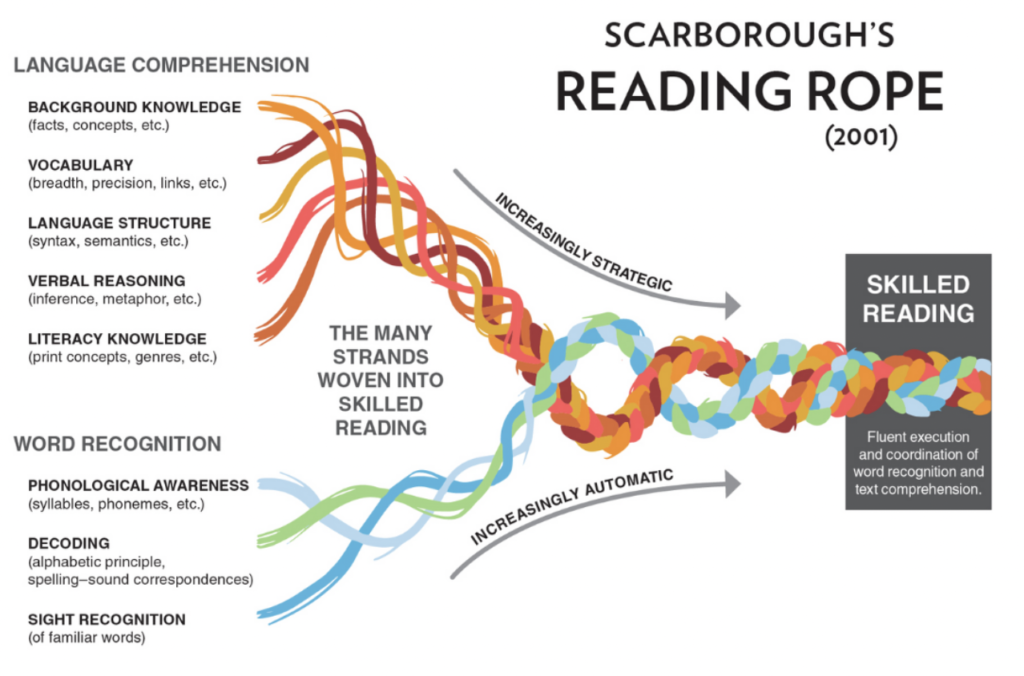
Before we begin, I would suggest you take a moment to truly study the image above and watch our video on Scarborough’s Rope.
The above is a beautiful metaphor for the skills necessary for proficient reading with comprehension created by Hollis Scarborough. This metaphor is commonly used in considering reading development in children, but regardless of age, the science of reading applies. Today, we will dig into this metaphor as it relates to adults.
Ask a group of tutors or teachers who work with adults on reading, and you would likely get a kaleidoscope of answers about what skills their students need and why. Understanding the components of reading can help each tutor or teacher identify the gaps in their student’s skills to better plan for lessons and assessments.

The elements of Scarborough’s Rope can be assessed formally and informally. The most commonly given assessments in adult literacy curriculum focus largely on word recognition skills, along with some language structure and vocabulary. While those are important, it is also key to assess the other skills that may not be so specifically measured. Below are some informal ways to assess each skill in adult students.
| Skill | Informal Assessment |
|---|---|
| Background Knowledge | Informal questions before reading a text Creating concept maps of topic Student self rating their knowledge of a topic |
| Vocabulary | Vocabulary assessment should be text specific Fill in the blank sentences Word Match Student rating word knowledge before, during, and after |
| Language Structure | Grammar Assessments on specific skills Written sentences or paragraphs Student editing |
| Verbal Reasoning | Creating metaphors and similes Making predictions based on evidence Comparing and Contrasting |
| Literacy Knowledge | Label the parts of a book or text (ie Title, headings, glossary, spine) Identifying the genre of the text being read Student identifies the purpose of reading a text |
| Phonological Awareness | Breaking a word into syllables List rhyming words |
| Decoding | Sounding out words that follow “the rules” Recognizing the sound of each letter Identifying blends and digraphs |
| Sight Recognition | Quickly identify common words in a text by highlighting Speed drills |
Formal assessments do exist for most of these skills. The curriculum you are using may have assessments built in. Be sure you understand the exact skill the assessment is measuring. Below is a list of other assessments available for free. Please always remember for an assessment to give you a clear picture of the student’s ability, you must administer it carefully and correctly. Read the directions and practice on a friend before giving any of these .
| Assessment Name | Skills Measured |
|---|---|
| San Diego Quick Assessment | Some sight words, Decoding |
| Quick Phonics Screener | Phonological Awareness, Decoding |
| Dolch and Fry Sight Word Assessments | Sight Recognition |
Teaching Strategies for Each Skill
Regardless of which skill you are teaching, it is absolutely imperative that the strategy used is relevant and appropriate for adults. Avoid childish materials or items with a grade level listed anywhere the student may see. Most adult literacy curriculum does this, but a tutor often needs additional materials or support for a skill. Be prepared to make adjustments.
Also, be sure to assess your own understanding of each skill and concept. Adult learners are going to great lengths to improve their reading. Accurate and clear instruction honors their time and goals.
| Skill | Teaching Strategy |
|---|---|
| Background Knowledge | Use images or short videos to build background knowledge Discuss each new topic at the end to add detail and nuance Use KWL Charts when reading on a new topic |
| Vocabulary | After a first reading, go back and identify new or unfamiliar words to the reader. This ensures lessons are not only on expected vocabulary, but also the needs of the reader. Practice using context clues and dictionaries (paper or online) in real time In a notebook have students build a journal of words they have learned that are relevant to their daily lives. |
| Language Structure | Explicitly teach grammar skills in isolation, and then identify them in a written passage. Include appropriate length written responses to text frequently. As skill develops, lengthen responses. Have students bring in forms or other writing necessary to their daily lives to practice |
| Verbal Reasoning | Find similes and metaphors in texts and discuss them. Do crossword puzzles Use graphic organizers to sort information from a text Discuss real life examples of the student making predictions. Give evidence for answers |
| Literacy Knowledge | Before beginning any text, point out the features of the text and explain the purpose of those features. |
| Phonological Awareness | Point out where in the mouth each sound is made. Manipulate words from the text – delete sounds, add sounds Using relevant words, practice orally breaking the words into syllables |
| Decoding | Use highlighters or colored pencils to identify new sounds or spelling patterns. |
| Sight Recognition | Flash cards for quick practice. Build an ongoing list of automatic words. |
We hope this post helps you get started addressing all the components of reading with your learners. Please subscribe to our network for future posts about each element, specific assessments, teaching strategies, and more! Also, go join the discussion about the elements of reading on our Arkansas Tutor Network Facebook Page.